Content

These statements, which include the Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flows, and Shareholders Equity Statement, must be prepared in accordance with prescribed and standardized accounting standards to ensure uniformity in reporting at all levels. In short-term decision-making, revenues are often easier to evaluate than costs. In addition, each alternative typically only has one possible one revenue outcome even though there are many costs to consider for each alternative. The starting point is to understand the various labels that are attached to costs in these decision-making environments. The incremental costs usually do not include fixed manufacturing costs.
- If timely and accurate information is not provided, the acquirer might underestimate or overestimate the company, which will be a great loss for the acquirer.
- %X We present a system for automatically extracting pertinent medical information from dialogues between clinicians and patients.
- Financial StatementFinancial statements are written reports prepared by a company’s management to present the company’s financial affairs over a given period .
- In conducting these types of analyses between alternatives, the initial focus will be on each quantitative factor of the analysis—in other words, the component that can be measured numerically.
- Suppose Beza Company owns a warehouse and can either use it to store products or rent it to another company for Br.8, 000 per year.
- The use of the word prior is a key indicator that information is nonrelevant to a current decision.
- The incremental revenue in this decision will be the price per unit offered by the potential customer times the number of units to be purchased.
In carrying out step three of the managerial decision-making process, a differential analysis compares the relevant costs and revenues of potential solutions. First, it is important to understand that there are many types of short-term decisions that a business may face, but these decisions always involve choosing between alternatives. In each of these situations, the business should compare the relevant costs and the relevant revenues of one alternative to the relevant costs and relevant revenues of the other alternative. Therefore, an important step in the differential analysis of potential solutions is to identify the relevant costs and relevant revenues of the decision.
Principle of relevant information for graph sparsification
This is a particular issue when determining the format and content of an entity’s financial statements, since the proper layout and level of detail of information can adjust the opinions of users regarding the future direction of a business. For example, the controller of a business chooses to add information to the financial statement disclosures regarding the cash flows being generated by its newest retail stores. This information is relevant to the decisions of the investment community, because it clarifies for them how well the entity is performing. Many stakeholders also use past financial statements to analyze the company’s future performance regarding profitability. Therefore any such false data doesn’t come under the definition of accounting relevance.

An avoidable cost is one that can be eliminated by choosing one alternative over another. For example, assume that a bike shop offers their customers custom paint jobs for bikes that the customers already own. If they eliminate the service, the cost of the bike paint could be eliminated. Also assume that they had been employing a part-time painter to do the work.
The access of relevant information for solving problems
Information provided by a State regarding its nuclear material and activities represent the great majority of information used by the IAEA for safeguards implementation. Short-term and long-term business decisions should be analyzed using different frameworks. Qualitative factors can significantly affect the manager’s decision. For example in make-or –buy decision, the quality of the product purchased externally, the reliability of supply sources, the expected stability of price over the next years, labor relations, community image and so on. Therefore, qualitative factors must be taken into consideration in the final step of the decision making model.
The first step in decision-making process is to recognize and define a specific problem. This is the most important stage because all other activities in the process depend on it. If one does not have a clear understanding of the specific problem, he/she may spend valuable time and energy in identify alternatives and gathering probably irrelevant data. Moreover, incorrectly defined problems waste time and resources.
Evaluating Sources
That is why it is usually said that defining a problem is solving 50 percent of the problem. Suppose a company has spent Br.500, 000 developing a new product. Problems have risen and the managers must now decide whether or not to market it. The Br.500, 000 is irrelevant to the decision because it is not differential; that is, the cost will be the same whether or not the firm markets the product. Similarly, depreciation on a machine is irrelevant in decision which products to make with that machine. All historical costs, whether original cost or book value , are sunk costs.
What is relevant information in decision-making?
Relevancy of an information
In the process of decision-making, a piece of information is said to be relevant if it is expected to be related to the future data that diverges among the various alternatives.
Accounting PrinciplesAccounting principles are the set guidelines and rules issued by accounting standards like GAAP and IFRS for the companies to follow while recording and presenting the financial information in the books of accounts. As per GAAP, the information should be useful, understandable, timely, and pertinent for end-users to make important decisions. Relevance level “Lower” – Information that is “twice removed” should usually not be included unless the other considerations described above are unusually strong. For example, in the above “John Smith” article, “Murderer Larry Jones was also a member of the XYZ organization.” Relevance level “High” – The highest relevance is objective information directly about the topic of the article.
Consider this concept in relation to Centralized vs. Decentralized Management and how a company’s approach may affect the decision-making process. Discuss possible short-term issues and decisions, management focuses, and whether or not the centralized versus decentralized style will aid in company flexibility and success. Also, think in terms of how the decision-making process will be evaluated. In such kind of decision, the contribution margin technique must be used wisely.
Why is relevant information important?
Relevant data is indisputable
If your organization wants to make decisions based on facts, having actionable data on-hand empowers you to answer any “why?” questions. To be crystal clear: relevant data reported correctly is indisputable.
Verify the authors’ qualifications with other sources, such as other journal articles they have written, or institution web pages where they work. Sources must be current, accurate, cover the topic thoroughly, and provide supporting evidence. Reliable sources are an expectation of of any good research assignment, especially college level research.
Opportunity costs
Using the space for storage requires that Beza forego the opportunity to rent it, which means that there is a difference to Beza if it chooses to take one action rather than another. When Beza considers any action that requires using the space for storage, the relevant cost of the space is its opportunity cost, the Br.8, 000 rent Beza will not collect. relevant information includes the predicted future costs and revenues that differ among the alternatives. Any cost or benefit that does not differ between alternatives is irrelevant and can be ignored in a decision. All future revenues and/or costs that do not differ between the alternatives are irrelevant. Financial StatementFinancial statements are written reports prepared by a company’s management to present the company’s financial affairs over a given period .
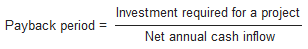
The joint product costs have already been incurred and therefore are sunk costs. However, allocation of joint product costs is need for some purposes, such as balance sheet inventory valuation. In case joint products are on hand at the end of an accounting period, some value must be assigned to them. To do so, joint product costs must be allocated to specific units of inventory. In addition, joint costs are also important for income determination. Sunk costs are most problematic for business decisions when they pertain to existing equipment.
